How to select the right DC Power Supply for DC Motors?
Motors, solenoids and relay controls require higher levels of current during start-up than they do for continuous operation. Mechanical failures such as motor stalls or due friction can increase the current draw dramatically. When designing or installing a DC motor supply, many factors such as back up, loading, speed variation, regenerative current and others should be considered. At Helios, we recommend that when selecting a power supply for your DC Motor, you should be aware of at least the following aspects:
- Maximum Current required: High currents drawn above the motor rating can cause motor seizures, overloads and motor failures causing heating and not rotating.
- Constant Current limit: Not one that goes into hiccup mode this means that, should an overload occur, the output current stays at its limit point, and the output voltage reduces towards zero. Typically, the supply will automatically return to its normal output voltage when the overload condition is no longer present.ie when the motor is running normally.
- Output diode required: To prevent the power supply being damaged by reverse voltage spikes which occur when the supply is turned off and the motor is slowing down.
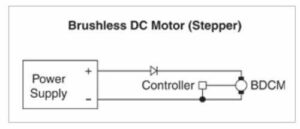
To illustrate, here are examples for brushed dc motor and a brushless dc motor
Brushed DC motors
With this type of motor, the magnets are stationary and the coil rotates. Electricity is transferred to the rotating coil by the use of “brushes”. The advantages of this type of motor are low initial cost and easy speed control.
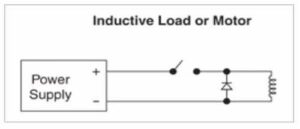
When the power is interrupted, the motor coil will act like an inductor and will try to continue to produce current, effectively becoming an inverted voltage source. This will apply a reverse polarity to the power supply and can cause damage to the motor. (Back EMF – Electro-Magnetic Flux)
By using a diode, as shown below, the diode provides a current path for the reverse motor current and will clamp the reverse voltage to a level no greater than the forward voltage drop of the diode. This protects the power supply’s output capacitors and other components from being stressed by the reverse voltage.